How to Find the Voltage of a Car Battery
- by Joe Weber - updated on 10/18/2024

Car batteries provide the quick jolt of power needed to start your engine. But over time, they lose efficiency and don't hold a charge as well as they did when they were new. That's why it's a good idea to check your battery's voltage every now and then to ensure it's still working efficiently. In this guide, we'll walk you through what voltage to look for and how to test it with a simple multimeter.
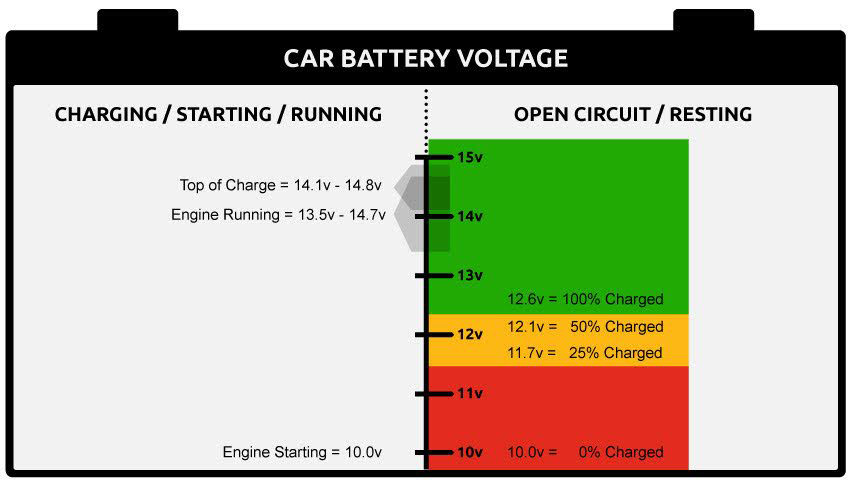
How Many Volts Should a 12-Volt Battery Have?
Most modern vehicles use a 12-volt battery, which consists of six cells, each holding 2.1 volts when fully charged. So, when your car's engine is off, a fully charged battery should read 12.6 volts or more. When you start your vehicle, the voltage will briefly drop, but a healthy battery should stay above 10V, even though colder weather can cause it to dip lower. Once the engine is running, the alternator kicks in to recharge the battery, and you should see a voltage between 13.5 and 14.7 volts.
What is the Minimum Voltage Needed to Start a Car?
Even a small drop in your battery's voltage can significantly impact its performance. As shown in the chart above, a voltage reading of 12.1V means your battery is only at 50% of its full charge. If your battery falls to 11.9V or lower, you'll start to notice a significant decrease in performance. When the voltage dips to 11.6V, the battery is almost fully discharged and may struggle to start your car.
How Many Volts Should a Car Battery Lose Overnight?
It's normal for a car battery to lose a small amount of charge overnight due to something called a parasitic draw. This refers to things like your car's clock, interior lights, radio settings, and alarm system that continue to use a little power even after the engine is off. Fortunately, the amount of power these applications use is minimal. In newer cars, you can expect a draw of 50 to 80 milliamps, which translates to about 0.05-0.08 volts. Older cars with fewer electronics typically use even less power.
If you have a car that sits unused for long periods, it's important to take steps to keep the battery charged. For more tips on how to prevent your battery from dying when not in use, check out our blog titled "How Do You Keep a Car Battery from Dying When Not in Use?"
What Are Some Other Factors That Affect Battery Voltage?
In addition to parasitic draw, several other factors can affect your battery's performance and lower its voltage. From extreme temperatures to frequent short trips, these issues can gradually wear down your battery. To learn more, check out our article on the Six Things That Can Drain Your Battery and discover practical steps you can take to help prevent them.
How Do You Measure Your Car Battery's Voltage?
You can measure your battery's voltage using a handheld tool called a multimeter. Just follow these simple steps:
- Turn off any additional power draws, including headlights, radio, air conditioning, GPS, etc.
- Perform the test after the car has been sitting with the engine off for a while.
- Wear proper safety gear like eye goggles and sturdy, waterproof gloves.
- Set the multimeter to voltage, and adjust it between 15 and 20 volts of DC (direct current) power. If your multimeter doesn't have specific settings, just select DC volts.
- Ensure the vehicle's ignition is off, then remove the battery cover.
- Clean any corrosion from both terminals to get good electrical contact.
- Attach the multimeter leads, the red lead to the positive terminal, and the black lead to the negative terminal.
Understanding Your Multimeter Results
If your battery reads between 12.4V and 12.7V, it's fully charged and ready to go. If the voltage is below 12.2V, it's time for a recharge—either take a 30-minute drive on the highway or use a charger to bring the voltage back up. However, if your voltage is higher than 12.9V, the battery is overcharged.
Overcharging can cause damage, so you'll want to reduce the excess current. You can do this by turning on your headlights to the high beam setting with the engine shut off for a short time, then retesting the battery to ensure it's back in the ideal range.
Batteries Plus Tests Vehicles Batteries for Free
If you don't have a multimeter, you can always swing by your local Batteries Plus. Our experts are happy to test your battery for free and find the best battery for your car or truck. We'll even install new car batteries on most makes and models. Want to save time? You can even schedule your arrival online to cut down on the wait.
Check out our guides on finding the best jumper cables and how to jump-start a vehicle using a portable power pack. Be sure to visit our Automotive Center for a wide selection of headlight bulbs, auto fuses, wiper blades, and more.